LINK 16
What is LINK 16?
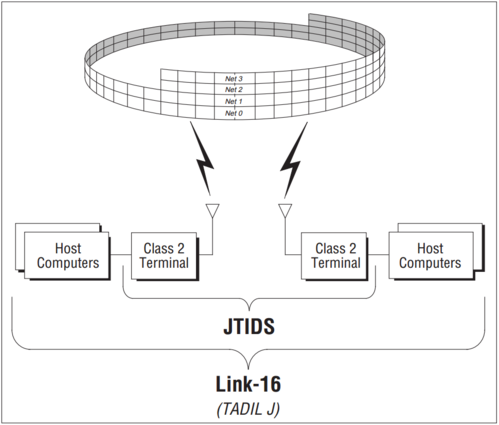
Link-16 is a high capacity, secure, jam-resistant, nodeless broadcast-type RF data link that uses a Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) protocol. It provides information distribution, position location, and identification capabilities in an integrated form for tactical military operations. Link-16 utilises the Joint Tactical Information Distribution System (JTIDS) or the Multi-Functional Information Distribution System (MIDS) terminals, and the protocols, conventions, and fixed word message formats defined by STANAG 5516. JTIDS/MIDS operates in the upper ultra high frequency Lx band.
How does LINK 16 work?
Link 16 operates in the UHF frequency band, providing line-of-sight and beyond-line-of-sight connectivity over considerable distances. It employs a TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) architecture, allowing multiple users to transmit and receive data on the same frequency without interference.
What are the 3 requirements to get into link 16?
- Correct crypto (Key)
- Network Design Load (NDL)
- Time synchronization (NTR)
Which F-16 Variants have LINK 16 implemented?
Check F-16 Variants.
What is a J-Series message?
- It is a template for data exchange that is programmed into the link 16 structure
- Its data fields are populated by transmitting aircraft and interpreted by receiving aircraft
LINK 16 Limitations in Falcon BMS
- Only C2 can provide SURV air track information.
- Secondary fighter air target tracks, Lock lines and AMRAAM shotlines are not currently implemented.
- Ground LINK 16 is not currently implemented.
LINK 16 PPLI vs Surveillance
- Add later
Acronyms
| Short form | Full form | Implemented in BMS | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor | Partially yes | For situational awareness during a mission, pilots may want to monitor aircraft or targets reported by aircraft that aren’t part of their flight or team. These aircraft, known as donors, can be designated during mission planning (via the Data Cartridge), or selection or deselection can be managed in the cockpit through the LINK 16 DNR page on the DED. Note: Secondary fighter air target tracks, Lock lines and AMRAAM shotlines are not currently implemented. | |
| FC | Fighter Channel | Yes | This Channel establishes the subnet on intraflight communications. This subnet is used to share ownship targets within a flight. The pilot would change the Fighter Channel to receive target information from aircraft that are operating on a different fighter-to-fighter subnet (e.g. different donors) or to join another flight. All members of the flight must select the same Fighter Channel; otherwise, the Link 16 target sorting messages from the flight members will not be received. The numerical value can be set between 0 and 126. |
| IDM | Improved Data Modem | Yes | The F-16's improved data modem is a crucial component of its avionics system, enhancing communication capabilities for both command and control purposes anddata transfer. The IDM facilitates seamless and secure transmission of various typesof data, including mission-critical information, sensor data, and tactical updates between aircrafts. IDM was designed in the late 70’s before LINK 16 was on the horizon of the aircraft manufactures. Even if limited in features compared to MIDS/JTIDS systems, it follows the same principle of exchanging data. |
| JDN | Joint Data Net | Yes | An interconnected network of JTIDS/MIDS based systems which links air and missile defence Command and Control and weapons systems across L16 capable forces. |
| JTIDS | Joint Tactical Information Distribution System | Yes | Refers to the communications component of Link-16. It encompasses the Class 2 terminal software, hardware, RF equipments, and the high-capacity, secure, antijam waveform that they generate. Among NATO subscribers, the equivalent term for JTIDS is the Multifunctional Information Distribution System (MIDS). |
| MC | Mission Channel | Yes | This Channel establishes the subnet on the C2 (e.g. AWACS or ABCCC) aircraft is operating. The control NPG is used by C2 to transmit assignments to the flight lead and for the flight lead to transmit responses and report assignment status. As a flight progresses to the target area, the controlling aircraft could change. When a controller change is required, the current controlling aircraft transmits a request for handover message to the flight indicating the new controllers subnet (i.e., MC). After accepting the handover request, the flight members change the mission channel to communicate with the new controller. The numerical value can be set between 0 and 127. |
| MIDS | Multifunctional Information Distribution System | Yes | See JTIDS |
| NDL | Network Design Load | Yes | This system used to initialize the JTIDS/MIDS terminal |
| NPG | Network Participation Groups | Yes | FC and MC channels are part of dedicated NPG’s. Each channel and its number define what data can be exchanged on that channel. If you create a package for example, all LINK 16 capable aircraft of this package will have the same FC and MC (because one AWACS controller will be responsible for this package). |
| PPLI | Precise Participant Location and Identification | Yes | PPLI air tracks are shared between aircraft sharing the same NPG. Each PPLI message contains an abundance ofinformation about a unit, including its detailed position andidentification information, its time quality, its IFF codes, and much more. |
| SC | Special Channel | Yes | This Channel establishes for SEAD NPG and identification information.The numerical value can be set between 0 and 126. |
| SURV | Surveillance | Yes | This message is used to share air trajectory data and is primarily disseminated by command and control agencies. |
LINK 16 Net Message Table (STANAG 5516)
| J | Series | Message | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| J0.0 | Network Management | Initial Entry | Provides the data elements, in a known time slot, required for net entry. |
| J0.1 | Test Message | Used for terminal test and performance evaluation. | |
| J0.2 | Net Time Update | Adjusts the system time to a standard time. | |
| J0.3 | Time Slot Assignment | Permits dynamic assignment of time slots. | |
| J0.4 | Radio Relay Control | Provides the means for the JU responsible for relay control to assign and deassign the paired slot radio relay function to a terminal and to control the relay function parameter. | |
| J0.5 | Repromulgation Relay | Requests that those messages in the same time slot containing the J0.5 message be relayed by all JUs receiving the message. | |
| J0.6 | Comm Control | Initiate or terminates specific transmissions to control communications, and requests network management actions. | |
| J0.7 | TSR Announcement | Provides the capability for a JU to request a percentage of time slots from a shared pool and disseminate the requests of other JUs. | |
| J1.0 | Connectivity Interrogation | Solicits direct or indirect connectivity of the addressed JUs to support route establishment. | |
| J1.1 | Connectivity Status | Disseminates direct or multilevel connectivity of the source JUs. | |
| J1.2 | Route Establishment | Establishes a route for relay/destination control. | |
| J1.3 | Acknowledgment | Used by a JU involved in ground-to-ground communications to respond to messages that require machine receipt/compliance. | |
| J1.4 | Communication Status | Used by JUs to report the connectivity quality of its direct communicants to Net Control Station (NCS) and other direct communicants. | |
| J1.5 | Net Control Initialization | Provides a number of initial terminal parameters required to allow a terminal to actively participate in an established net under the control of a dynamic net manager | |
| J1.6 | Needline PG Assignment | Used by the designated NCS to assign an addressed JU its associated destination Source Track Numbers (STNs) with Participation Group (PG) numbers to form Needline PGs. | |
| J2.0 | Precise Participation Location & Identification (PPLI) | Indirect Interface Unit PPLI | Provides Participating Unit/Reporting Unit/Generic Unit information on the Link 16 network when network participation status, identification, and positional information is forwarded from Link 11/11B. |
| J2.2 | Air PPLI | Provides all JUs information about airborne JUs on the Link 16 network. It is used by airborne JUs to provide network participation status, identification, positional information, and relative navigation information. | |
| J2.3 | Surface (Maritime) PPLI | Provides all JUs information about surface JUs on the Link 16 network. It is used by surface JUs to provide network participation and relative navigation information. | |
| J2.4 | Subsurface (Maritime) PPLI | Provides all JUs information about subsurface JUs on the Link 16 network. It is used by subsurface JUs to provide network participation status, identification, positional information, and relative navigation information. | |
| J2.5 | Land (Ground) Point PPLI | Provides all JUs information about stationary ground JUs on the Link 16 network. It is used by stationary ground JUs to provide network participation status, identification, positional information, and relative navigation information. | |
| J2.6 | Land (Ground) Track PPLI | Provides all JUs information about mobile ground JUs on the Link 16 network. It is used by mobile ground JUs to provide positional information, and relative navigation information. | |
| J3.0 | Surveillance | Reference Point | Used to exchange tactical information about geographic references. |
| J3.1 | Emergency Point | Provides the location and type of an emergency that requires search and rescue. | |
| J3.2 | Air Track | Used to exchange information on air tracks. | |
| J3.3 | Surface (Maritime) | Used to exchange information on surface tracks. | |
| J3.4 | Subsurface (Maritime) Track | Used to exchange information on subsurface tracks and Datums. | |
| J3.5 | Land (Ground) Point/Track | Used to exchange tactical surveillance information on land points and tracks. | |
| J3.6 | Space Track | Exchanges information on Space and Ballistic Missile tracks. | |
| J3.7 | Electronic Warfare Product Information | Provides the means to exchange tactically significant information that has been derived from electromagnetic sources. | |
| J5.4 | Anti Submarine Warfare | Acoustic Bearing/Range | Used to report acoustic bearing and range of subsurface contacts. |
| J6.0 | Intelligence | Intelligence Information | Provides the means to exchange tactically significant information that has been derived from electromagnetic sources. |
| J7.0 | Track Management | Track Management | Used to transmit information necessary to effect management actions on tracks being reported within the interface. Management actions include dropping tracks, reporting environment/category and identity conflicts, changing environment/category and identity, changing alert status, and changing strength. |
| J7.1 | Data Update Request | Used to request tactical information that has been locally generated by units participating within the interface. | |
| J7.2 | Correlation | Used to resolve a dual designation problem by identifying one track to be retained and another to be dropped. | |
| J7.3 | Pointer | Used to transmit a geographic position to an addressed unit within the interface. | |
| J7.4 | Track Identifier | Used to transmit special identification numbers associated with the reference track number (TN). | |
| J7.5 | IFF/SIF Management | Used to transmit Identification Friend or Foe/Selective Identification Feature (IFF/SIF) information or a special code on a referenced track. Provisions are available to obtain the most current information by exchanging, clearing, or updating IFF/SIF data between units within the interface. | |
| J7.6 | Filter Management | For foreign agency use | |
| J7.7 | Association | Used to transmit information, on two or more TNs, that has been automatically or manually associated when the information is deemed to pertain to the same contact. When a determination is made that the relationship above no longer exists, there is a provision for terminating this information association. | |
| J8.0 | Unit Designator | Used to transmit to a terminal (from its NCS) the unit designator associated with the TNs in the terminal’s Participation Group assignments. The message will also be used to inform an NCS of a terminal’s unit designator. | |
| J8.1 | Mission Correlation Change | Used to add, delete, or change Mission Correlators on a specific aircraft or flight of aircraft. | |
| J9.0 | Weapons Coordination & Management | Command | Provides the means to transmit threat warning conditions, alert states, and weapons condition orders, to direct weapon system engagement for air defense and air support, and to direct Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) operations. |
| J9.1 | Engagement Coordination | Provides the means for two or more elements to coordinate engagement, to conduct more efficient engagement, and to reduce the probability of wasted resources. | |
| J10.2 | ECCM Coordination | Provides the status of an engagement between the Reference TN and the Target TN. | |
| J10.3 | Handover | Used to transfer control of aircraft and remotely piloted vehicles/missiles between controlling units. | |
| J10.5 | Controlling Unit Report | Used to identify the JU that is controlling the track and to provide the Mission Correlator and/or voice call sign. | |
| J10.6 | Pairing | Provides a means to indicate a pairing (not engagement status) between a friendly track and another track or point | |
| J11.0 | Weapon Response/Status (1) | Provides weapon compliance responses to controller directives. | |
| J11.1 | Weapon Directives (1) | Provides controller directives to a weapon. | |
| J11.2 | Weapon Coordination (1) | Used to coordinate the transfer of control authority and the delegation of third party source. | |
| J12.0 | Control | Mission Assignment | Used by C2 JUs and optionally by nonC2 JUs to assign missions, designate targets, and provide target information to nonC2 platforms. NonC2 JU acknowledgement of this message is through Receipt/Compliance (R/C) action. |
| J12.1 | Vector | Used by C2 JUs to send vector information and vector discretes specifically to air units operating on its net. Vectors are given for interception of air targets, navigation, and air traffic control. | |
| J12.2 | Precision AC Direction | Used by controlling units for operations requiring precise control positioning of mission aircraft (for example, ground-directed release of ordinance, automatic carrier landing operations, etc.) | |
| J12.3 | Flight Path | Used by controlling units to provide air units with multiple-leg flight path information. | |
| J12.4 | Controlling Unit Change | Used to provide new control agency information to an aircraft prior to handoff to the new control agency. It is also used by a tactical aircraft to initiate control procedures with a new controlling unit or to effect a change of controlling unit in response to a Controlling Unit Change (CUC) Order or by a C2 JU to initiate control by own unit. | |
| J12.5 | Target/Track Correlation | Used by controlling C2 JUs to:
| |
| J12.6 | Target Sorting | Used to:
JUs and from nonC2 JUs to C2 JUs, and;
| |
| J12.7 | Target Bearing | Used by nonC2 JUs to:
range, bearing, elevation, rate, and uncertainty data, and;
| |
| J13.0 | Platform & System Status | Airfield Status | Reports operational status of airfields, runways, airfield facilities, and aircraft carrier flight decks. |
| J13.2 | Air Platform Status | Provides the current status of an air platform including ordnance load, fuel, operational status, and on-board systems’ status. | |
| J13.3 | Surface Platform Status | Provides the current status of a surface platform including ordnance load, operational status and on-board systems’ status. | |
| J13.4 | Subsurface Platform Status | Provides the current status of a subsurface platform to include operational status and on-board systems’ status. | |
| J13.5 | Land Platform Status | Provides the current operational weapons and equipment status of a land platform. | |
| J14.0 | Electronic Warfare | EW Parametric | Provides the means to exchange parametric information that has been derived from electromagnetic sources. |
| J14.2 | EW Coordination & Control | Provides the means for Electronic Warfare (EW) participants to coordinate EW activities among themselves. | |
| J15.0 | Threat Warning | Threat Warning | Provides the capability for threat warning to targeted friendly platforms, including Threat Type, Threat Posture, Position/Relative Position, Altitude, and Speed. |
| J16.0 | Imagery | Provides the capability to transmit and receive imagery. | |
| J17.0 | Weather over target | Provides the current weather conditions over a target area. | |
| J28.0 | National Use | US National 1-Army | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. |
| J28.1 | US National 2-Navy | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.2 | US National 3-USAF | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.3 | US National 4-USMC | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.4 | FR National 1 | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.5 | FR National 2 | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.6 | US National 5-NSA | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J28.7 | UK National 1 | Purpose is defined by country and service of user. | |
| J31.0 | Miscellaneous | OTAR Management | Used to exchange cryptonet management information for rekeying the KGV-8 (Thornton). |
| J31.1 | OTAR | Used to transmit the new cryptovariables. | |
| J31.7 | No Statement | Used to fill out the remainder of a transmission opportunity when the messages to be transmitted do not require the full number of Reed Solomon code words. | |
| RTT-A | Round Trip Timing | RTT Addressed | Provides the means for a terminal to synchronize with system time using the active synchronization procedure. A specific terminal is interrogated and responds with the RTT Reply. |
| RTT-B | RTT Broadcast | Provides the means for a terminal to synchronize with system time using the active synchronization procedure. The RTT-B is not addressed to any particular terminal. Any terminal that meets the specified requirement for time quality level responds with the RTT Reply. | |
| RTT-REP | RTT Reply | Provides the means for a terminal to support the active synchronization procedure of another JU by providing time-of-arrival data in response to either an RTT-A or RTT-B Interrogation. |
Reference Sources
- MR-1235-AF | Interoperability - A Continuing Challenge in Coalition Air Operations | By Rand | ISBN 0-8330-2912-6
- Understanding Link-16 - A Guidebook for New Users (Link-16 system) (Ver 3 - Sep 2001) | By Northrop Grumman
- Understanding Voice and Data Link Networking - Northrop Grumman's Guide to Secure Tactical Data Links (Dec 2014) | By Northrop Grumman